Did you know that magnesium, found naturally in many foods and supplements, could be the key to better sleep? While more research is needed to fully understand its impact, studies suggest that magnesium might positively influence sleep quality.
Experts theorize that magnesium works its sleep magic by lowering cortisol, the stress hormone, boosting melatonin, a hormone that promotes sleep, and regulating neurotransmitters in the central nervous system (CNS).
This article dives into how magnesium could improve your sleep, its other benefits, how to incorporate it into your routine, and which foods are rich in this essential mineral. Plus, it weighs the risks of excessive magnesium intake and compares it to melatonin.
Ready to catch some Z’s? Let’s explore the surprising benefits of magnesium for sleep together!
What is Magnesium?
Magnesium stands as a pivotal mineral within the human body, indispensable for a myriad of physiological functions. Its roles span from facilitating nerve and muscle function to fostering bone development, regulating blood sugar levels, and maintaining cardiac rhythm regularity. Moreover, emerging research underscores its significance in promoting restorative sleep patterns.
Ensuring adequate magnesium levels necessitates a balanced diet replete with magnesium-rich foods. For those concerned about meeting recommended intake levels, dietary supplements offer a supplementary avenue. The daily recommended magnesium allowance for adults, contingent upon age, gender, and pregnancy status, typically ranges between 310 and 420 milligrams.
How does Magnesium Effects Sleep
To understand how magnesium affects sleep, researchers are digging deeper. They believe magnesium might boost sleep quality in a few ways:
1. Regulating GABA: Magnesium could help control GABA, a brain chemical that calms the nervous system. By doing so, it might promote relaxation and act as a sedative to help you doze off.
2. Relaxing Muscles: Magnesium might also put the brakes on another brain chemical, called the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor. This could help your muscles chill out, promoting overall relaxation and better sleep.
3. Boosting Melatonin: Some studies suggest that low magnesium levels are linked to reduced melatonin, the hormone that regulates your body’s day-night cycle. By promoting melatonin production, magnesium could help regulate your sleep-wake rhythm, making it easier to fall asleep when you’re supposed to.
4. Lowering Cortisol: Magnesium might also help dial down cortisol, the stress hormone that keeps you on high alert. By reducing cortisol levels, magnesium could help you feel calmer and improve your sleep.
While more research is needed to fully understand magnesium’s role in sleep, these findings shed light on its potential benefits for catching those Z’s.
Benefits of magnesium:
Magnesium deficiency can up a person’s risk of illness. Magnesium might help out in these ways:
- Lowering the risk of type 2 diabetes: If you chow down on magnesium-rich foods, you could slash your odds of getting type 2 diabetes. But whether magnesium supplements help folks with diabetes manage their blood sugar better needs more research.
- Lowering blood pressure: A diet packed with magnesium might bring down your blood pressure, which is good news for folks dealing with hypertension. There’s an old study that says magnesium supplements could help too, but just a bit.
- Reducing migraine headache symptoms: If you’re low on magnesium, you might be more prone to getting migraine headaches. There’s a study suggesting that taking 300 mg of magnesium twice a day could help prevent migraines, either on its own or with other meds. But hold up, before you pop those pills, talk to your doc first. Taking that much magnesium might go over the daily limit, which could lead to some side effects.
- Reducing the risk of osteoporosis: Magnesium isn’t just good for sleep and headaches; it’s also a bone booster. It could bump up bone density and mess with levels of vitamin D and parathyroid hormone, both of which are important for bone health. So, loading up on magnesium-rich foods or taking supplements could help keep osteoporosis at bay.
- Relief from Insomnia: Feeling restless at night? Magnesium might lend a hand. Some studies hint that taking magnesium supplements could ease insomnia, that pesky problem where you can’t fall asleep or stay asleep. In one study, folks in their 60s snoozed longer, spent less time tossing and turning in bed, and even scored lower on an insomnia scale after taking magnesium.
- Effective for Restless Legs Syndrome: Ever heard of restless legs syndrome? It’s when your legs feel all jumpy and uncomfortable, making it hard to catch some shut-eye. Turns out, magnesium supplements could be the ticket to calming those restless legs down. Research shows that magnesium might be especially helpful for leg cramps at night, especially during pregnancy when low magnesium levels could be the culprit.
Using Magnesium:
Alright, when it comes to taking magnesium supplements, it’s important to stick to safe levels since we already get magnesium from our food, drinks, and sometimes meds.
Here’s the deal on daily doses of magnesium supplements, measured in milligrams (mg), for different age groups:
– Babies up to 12 months: It’s not safe to give them magnesium supplements.
– Toddlers aged 1 to 3 years: Stick to 65mg.
– Kids aged 4 to 8 years: Aim for 110mg.
– Teens aged 9 to 18 years: Shoot for 350mg.
– Adults aged 19 years and older: Keep it at 350mg.
Remember, it’s always best to chat with a healthcare pro before starting any new supplements, especially for kiddos.
Magnesium Rich Foods:
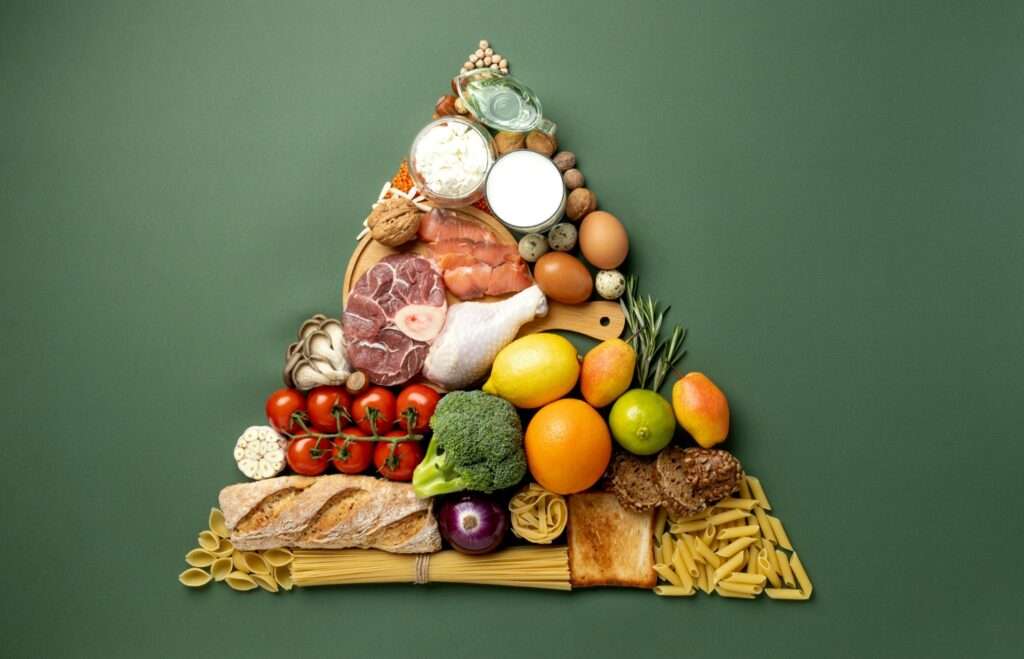

When it comes to getting magnesium from your diet, you’ve got plenty of options. Check out these foods that are packed with magnesium. Adding more magnesium to your diet is as easy as enjoying these tasty foods:
- Dairy: Think milk and yogurt.
- Fish: Halibut and salmon are great options.
- Fruits: Snack on apples, avocados, bananas, dried apricots, and raisins.
- Legumes: Black beans, edamame, kidney beans, and peas are all good sources.
- Meat: Beef and chicken breast can also help you get your magnesium fix.
- Nuts: Almonds, cashews, and peanuts make for crunchy snacks.
- Seeds: Chia and pumpkin seeds are tiny powerhouses.
- Soy: Try soy flour, soymilk, or tofu for a boost.
- Veggies: Load up on broccoli, carrots, and spinach.
- Whole grains: Brown rice, millet, oatmeal, and whole-wheat bread are all good choices.
Just mix and match these foods to create delicious meals that’ll give your magnesium levels a boost! Plus, some breakfast cereals and other foods have magnesium added by manufacturers. So, if you’re aiming to up your magnesium intake, mix and match from these sources to keep things tasty and nutritious!
Types of Magnesium for Sleep:
When it comes to using magnesium for sleep, different types of supplements offer various benefits. Here are a few that could support a restful night:
- Magnesium citrate: Often used to relieve constipation, magnesium citrate may also aid in improving sleep quality, particularly in older adults seeking better rest.
- Magnesium glycinate: Known for its potential in alleviating depression symptoms, including sleep disturbances, magnesium glycinate is highly absorbable, making it an effective option for promoting better sleep with minimal side effects.
- Magnesium L-threonate: While requiring further research, magnesium L-threonate shows promise in enhancing cognitive function and reducing anxiety, potentially contributing to improved sleep.
- Magnesium oxide: Although less easily absorbed compared to other forms, magnesium oxide has demonstrated efficacy in addressing sleep issues among older individuals, suggesting its potential usefulness for sleep support.
Magnesium and Melatonin
Magnesium is this mineral we get from our food, while melatonin is a hormone our brain cooks up. They’re both big shots when it comes to sleep, helping us doze off and keeping our sleep schedules in check. And hey, if you need a little extra, you can grab them in pill form.
When it’s lights out, our brain cranks up the melatonin, sending us straight to dreamland. That’s why some folks pop melatonin pills, especially after a long trip, to get back on track.
Now, magnesium isn’t directly responsible for making us sleepy, but it still lends a hand by messing with other brain chemicals, like melatonin. So, keeping our magnesium levels in check – whether through food or supplements – can mean smoother sailing to dreamland.
Side Effects and Risks:
While magnesium is generally considered safe, consuming too much of it can pose risks. Normally, your kidneys filter out excess magnesium, which is then excreted in urine.
However, in rare cases, excessive magnesium intake, especially from supplements or medications, can lead to various health issues, including:
– Diarrhea
– Nausea and vomiting
– Abdominal pain
– Urinary retention
– Lethargy
– Muscle weakness
– Magnesium toxicity
– Breathing difficulties
– Low blood pressure
– Irregular heartbeat
– Cardiac arrest
– Abdominal cramps
– Difficulty emptying the bladder or having a bowel movement
– Weakness
It’s essential to be aware of your magnesium intake and to consult with a healthcare professional if you experience any adverse effects.
Conclusion:
Magnesium, whether from a magnesium-rich diet or supplements, holds promise in promoting improved sleep quality.
While the exact mechanisms aren’t fully understood, research suggests magnesium aids relaxation by influencing neurotransmitters, lowering cortisol, and boosting melatonin levels.
However, excessive magnesium intake may lead to side effects and potential health issues, including interactions with medications.
As a vital mineral for nerve and muscle function, magnesium’s potential in enhancing sleep extends to alleviating anxiety and depression, soothing the central nervous system, and addressing sleep disorders.
Although studies on magnesium’s impact on sleep in humans are limited, consulting a healthcare provider before supplementing is crucial. They can identify underlying health conditions affecting sleep and provide tailored recommendations.
FAQs:
1. Does Magnesium help with sleep?
Yes, magnesium can definitely help you catch some Z’s. It’s all about relaxation – magnesium works its magic by calming your nerves, lowering stress hormones like cortisol, and boosting melatonin, the sleep hormone.
2. Does Magnesium Have Any Side Effects?
Well, magnesium is pretty safe, but too much can lead to some not-so-fun stuff like diarrhea, nausea, and tummy pains. Plus, it might not play nice with certain meds, so it’s smart to chat with your doc before going overboard with magnesium supplements.
3. What Foods Are High in Magnesium?
If you’re looking to load up on magnesium naturally, think green leafy veggies like spinach, whole grains, nuts, seeds, dairy, fish, fruits like bananas and avocados, and meats like chicken and beef.
4. How Much Magnesium Should I Take?
It varies based on things like your age and gender, but for adults, aim for around 310 to 420 milligrams a day. But hey, everyone’s different, so it’s always a good idea to touch base with your doc to figure out what’s right for you.
By: Well and Fit Life
